Git hub project url : https://github.com/phusion/passenger-python-flask-demo.git
Go to user home directory where you have to clone the repository. You can clone the repository from the below command as a user.
git clone https://github.com/phusion/passenger-python-flask-demo.gitNote : You can also clone the repository from Webuzo Enduser Panel > Server Utilities > Git TM Version Control
If Flask is not installed you can install it with pip binary given in the add application wizard as below.
/usr/local/apps/python3/bin/pip3 install flaskThe Passenger WSGI file
Create a WSGI file in the app's directory. Passenger expects it be called passenger_wsgi.py. The contents depends on the application and the web framework, but for our Flask example app, this is what you need to put in the file:
# passenger_wsgi.py
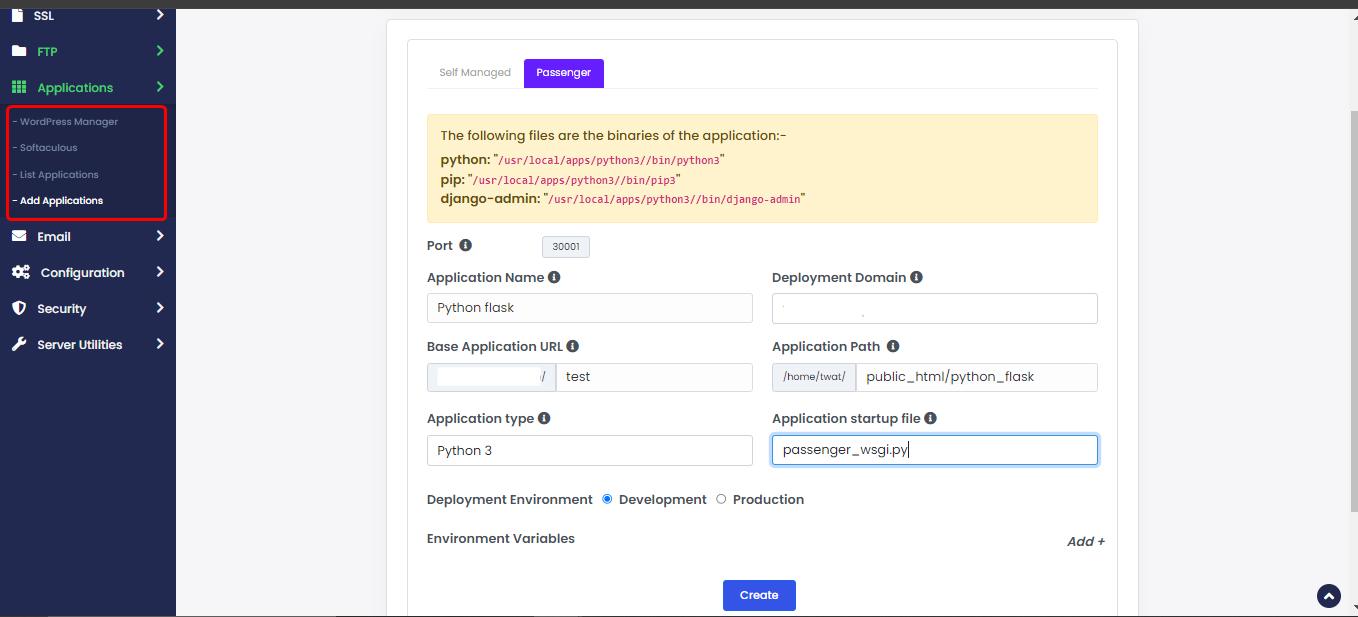
from app import MyApp as applicationTo add python application go to Webuzo Enduser Panel > Applications > Add Applications > Passenger Tab
Note : Before adding the application change the port in your project as given in "Add application" wizard.
For example in this application change "MyApp.run()" to "MyApp.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=30001, debug=True)" in manage.py
Fill the required fields, select python from "Application type" drop down and save it.
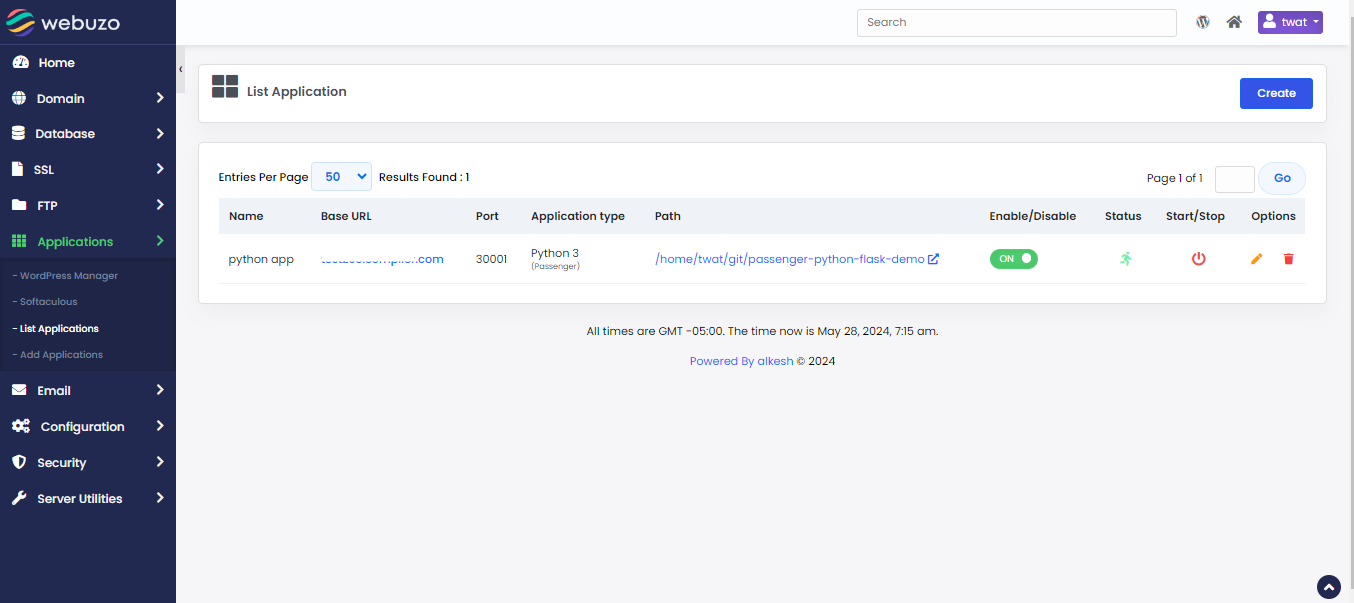
After saving it will be show in "List Applications" wizard.
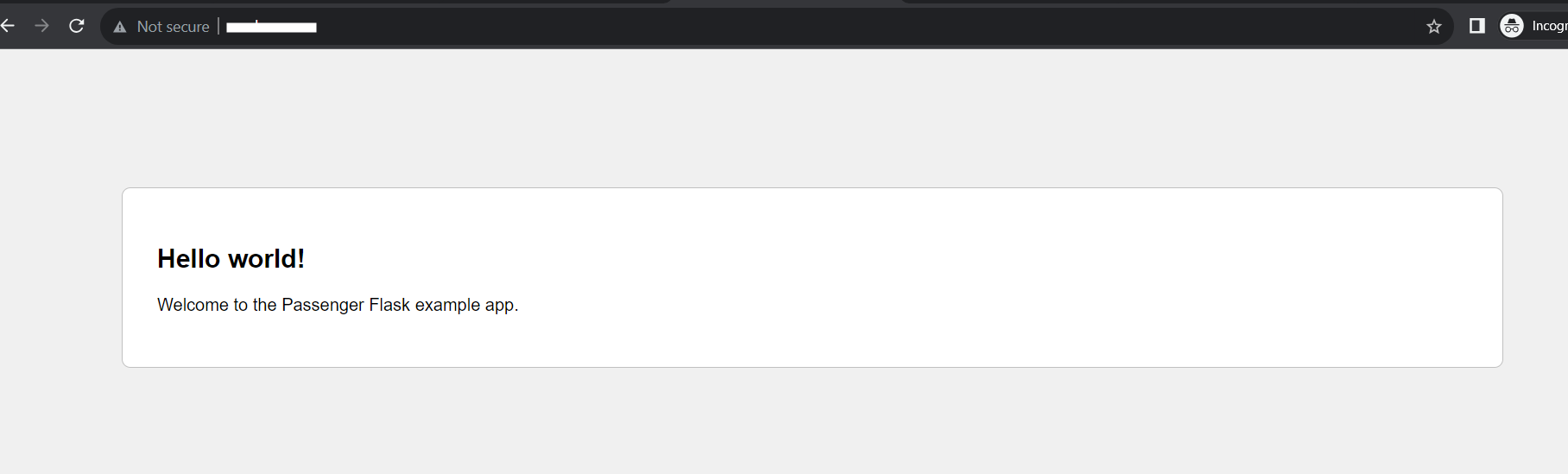
After the adding application check the domain in browser
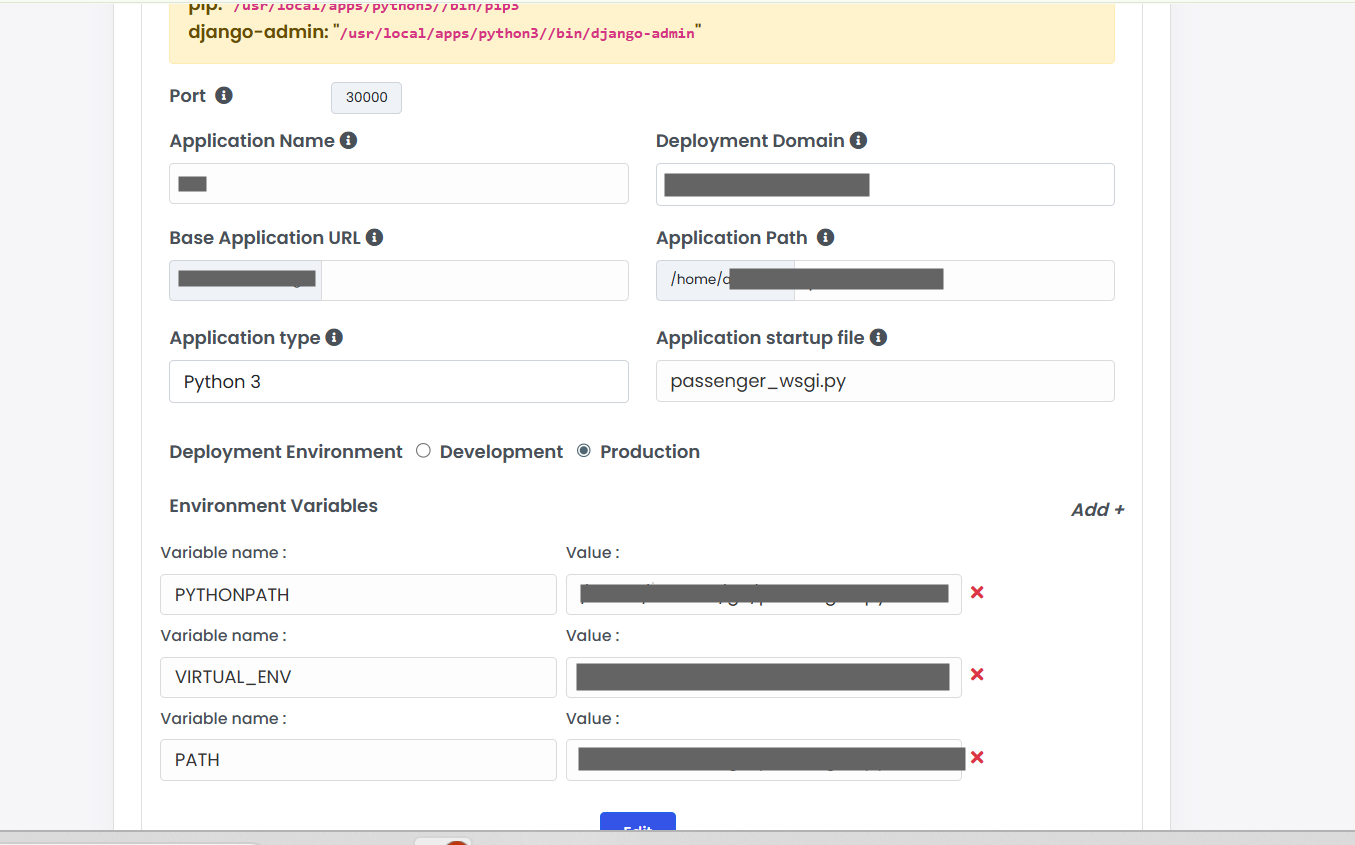
Note:
By default, your app will run using the system Python and system module paths.
If you want your app to use a virtual environment (venv) (so it runs with your venv Python and loads all modules from that venv), you need to add a few environment variables when creating the application.
PYTHONPATH /path/to/venv/lib/python3.x/site-packages
VIRTUAL_ENV /path/to/venv
PATH /path/to/venv/bin:$PATH
You can confirm if your app is using your virtual environment by printing the Python executable path inside your app, for example:
import sys
print(sys.executable)